What is Acne?
Acne is a skin condition that occurs when your skin pores are blocked by oil, bacteria, dead skin cells, and/or dirt. The oil glands under our skin release sebum(oil), which normally travels up hair follicles (also known as our pores) and onto the surface of our skin, keeping our skin soft. However, a build-up of oil, bacteria, or dead skin cells trapped in our pores can lead to inflammation. Acne is a physical manifestation of this inflammation.
Main Factors that Cause Acne
- Excess Sebum Production
- Hyperkeratosis (excess skin cell shedding in the hair follicle or pore)
- Over-Colonization of Propionibacterium Acnes (P.Acnes bacteria)
- Inflammation as part of the immune response to the bacteria
- Hormonal Influence
- Immune Response
Acne Pathogenesis
Excess Sebum Production - Hormone Imbalance
The sebaceous gland is located next to the hair follicle. Ideally, the sebum it produces moves along
the hair shaft to the skin’s surface, where it contributes to the lipid barrier that both lubricates and
protects the skin from environmental damage. Since sebum production is influenced by hormones,
particularly androgens such as testosterone, hormonal imbalances which can occur monthly or at
certain life stages, (ie. puberty) can lead to excessive sebum production. While most sebum reaches
the surface, in acneic skin, the sebum becomes trapped within the follicle.
Hyperkeratosis (excess skin cell shedding)
People with acne-prone skin shed up to five times more dead skin cells (corneocytes). These dead
skin cells should shed naturally, however in acne-prone skin, the process of shedding dead skin
cells (keratinocytes) becomes disrupted. Acne-prone pores are stickier, making it harder to shed
dead cells. This condition is known as retention hyperkeratosis, where dead cells accumulate in the
hair follicles and mix with sebum, leading to clogged pores. The trapped oil serves as a nutrient for
bacteria, creating an ideal environment for Cutibacterium Acnes (C.Acnes, formerly known as
Propionibacterium Acnes or P. Acnes) to increase and cause inflammation.
C. Acnes Bacterial Proliferation
Cutibacterium Acnes (C.Acnes) is a type of bacteria commonly found on the skin. Under normal
conditions, it exists as part of the skin's natural microbiome. When pores are blocked with excess
sebum and dead skin cells, C. acnes can multiply in this anaerobic environment, contributing to
inflammation, causing the characteristic redness, swelling, and pus associated with acne lesions.
Inflammation
When Cutibacterium Acnes (C.Acnes) bacteria overpopulate the hair follicles, it contributes to the
genesis of inflammatory acne. Our body’s natural response to this bacteria is to send white blood
cells to the source in order to ‘fight’ it and prevent any nasty infections. Once our white blood cells
have ‘killed’ the bacteria, they remain in your pores and are, essentially,
‘dead’ (pus is literally just a bunch of dead white blood cells).
Hormonal Influence
Hormonal fluctuations, especially an increase in androgens, further stimulate sebaceous gland
activity, making hormonal changes a key driver of acne, particularly during puberty, menstrual
cycles, pregnancy, or due to certain medications.
Immune Response
The body's immune system reacts to the bacterial activity and clogged pores, resulting in further
inflammation. The immune response can exacerbate the severity of acne, particularly in individuals
with inflammatory acne types such as cystic or nodular acne.
When Does Acne Begin?
Acne commonly begins during puberty, typically between the ages of 10 and 13, although it can start
earlier or later for some individuals. The onset is influenced by hormonal changes that occur during
this time, leading to increased sebum production and skin cell turnover.
While puberty is the most common period for acne to develop, it can also appear:
- In Early Childhood: Some infants may experience a form of acne known as neonatal acne,
which usually resolves on its own.
- In Young Adults: Many people experience acne into their late teens and early twenties, and for
some, it can persist into their thirties or beyond.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Acne can also be triggered by hormonal changes related to menstrual
cycles, pregnancy, or conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Overall, while puberty is the primary phase for the onset of acne, various factors can influence its
development at different life stages.
Let’s talk about the most common time for acne to appear: puberty, when the body starts producing androgens such as testosterone. In the skin, an enzyme converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone, which stimulates the sebaceous glands (oil-producing glands) to produce sebum (an oil-like substance). Boys experience a significant increase in testosterone levels during puberty, typically beginning around ages 9 to 14. Girls in their teens also experience an increase in testosterone, but to a greater extent in estrogen. Both of these hormone increases lead to more sebum production.
In individuals prone to acne, the increase in sebum triggers a condition called retention hyperkeratosis, where dead skin cells don't shed properly, leading to clogged follicles.
So, with all of this happening, it's time to look at the genesis of a pimple! Oil production is increasing, and dead skin cells are not shedding properly, leading us to the first stage: the formation of the microcomedone. As the dead skin cells begin to accumulate inside the pore, they become sticky and get trapped. Acne is an inflammatory condition, and the severity of the condition will determine the type of acne lesion that forms.
Below is an illustration of the life cycle of pimples.
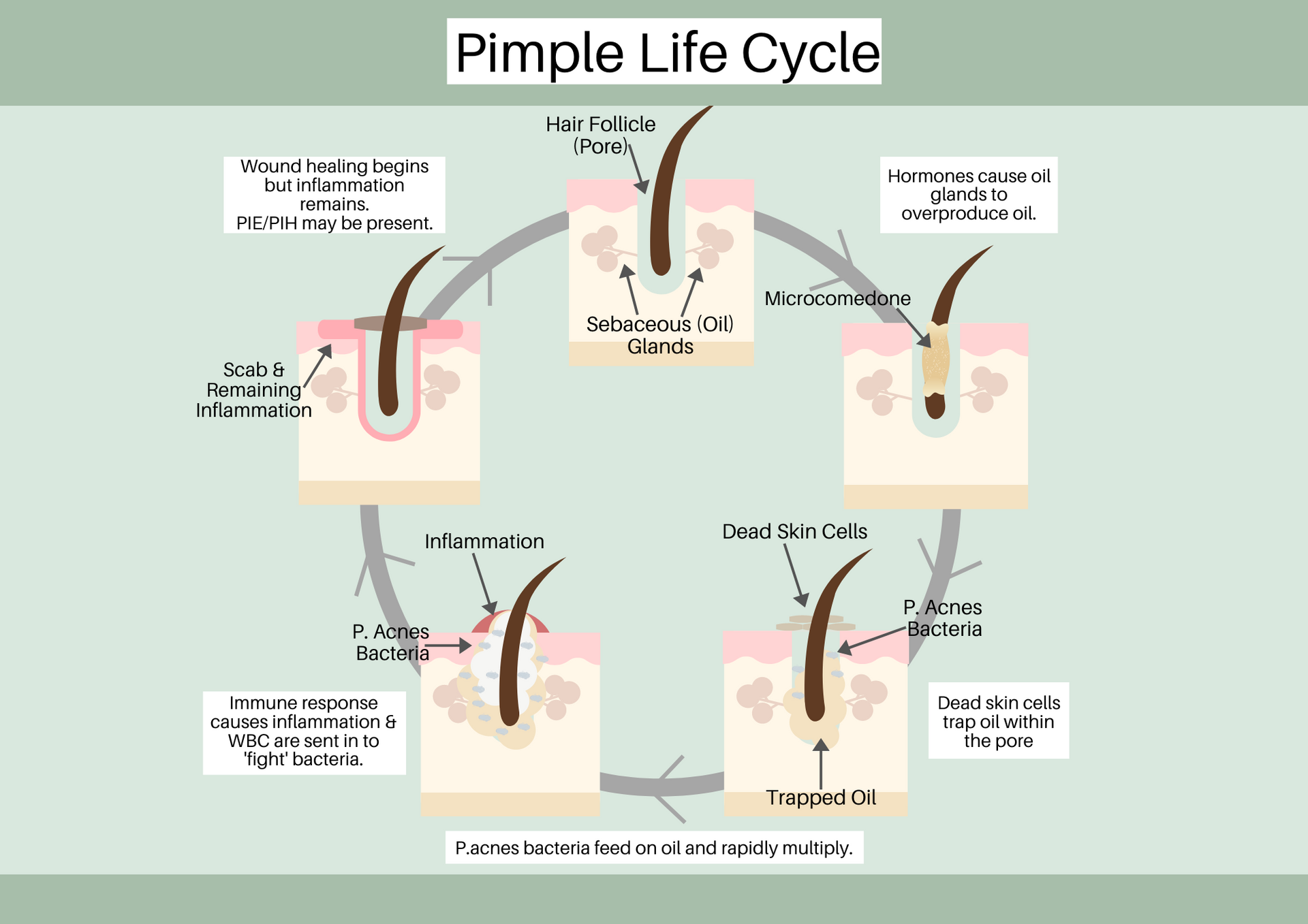
WBC - White Blood Cells
PIE - Post Inflammatory Erythema
PIH - Post Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
So, folks, there are four goals to battling acne. They are:
1. Reducing Oil Production:
Less oil means less chance for breakouts. Certain treatments and
products can dial down an individual’s skin’s oil production, making it harder for acne to set up
camp.
2. Boosting Skin Cell Turnover:
Regular exfoliation increases individuals’s skin cell turnover rate,sweeping away dead cells making it less possible for them to get clogged in pores.
3. Battling Bacteria:
Antibacterial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory products are our friends here.
Thankfully, times have changed and we have serums that can achieve all of this. And lastly, in some
cases oral antibiotics can help with fighting off bacteria..
4. Reducing Inflammation:
Many treatments and products focus on calming inflammation and
removing redness and swelling.